Overview
Overview
The brain is not the first part of the body to development. The heart begins beating before almost everything else. A developing brain needs a good circulatory system.
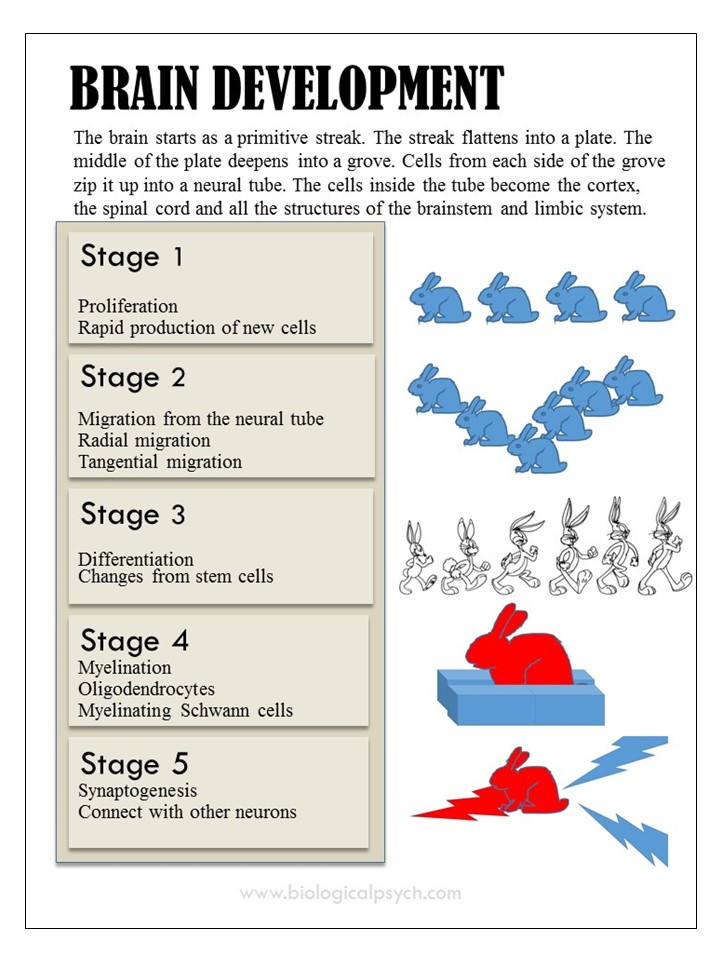
The brain begins as a primitive streak. The streak flattens out and its edges roll up, forming a neural tube. Without the important step, the brain and spinal cord will not develop properly.
Pay particular attention to how plasticity plays an important part throughout development.
Learning Objectives
By the end of this module, you should be able to:
- Describe the pathfinding process of axon development
- Describe the most common terlies atogens and their potential impact
- Explain plasticity and how it applies to the brain
- Describe how brain damage and reovery progress
- Compare and contrast neuron migration and apotosis
Readings
- Kalat C4
- Brain Development
Slides
Videos
Discussion
Quiz (not the same as on Canvas)
Written Assignment
- Describe the five (5) steps of neuron development.
- Define brain damage (open and closed) and how plasticity and sprouting can impact it.
- What did you find difficult or confusing in this chapter? If nothing was difficult or confusing, what did you find most interesting?
Study Aids
Key Terms
- altruistic behavior
- apoptosis
- artificial selection
- autosomal genes
- cerebrovascular accident
- chromosomes
- closed head injury
- collateral sprouts
- deafferented
- denervation supersensitivity
- deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
- diaschisis
- differentiates
- dizygotic
- dominant
- edema
- epigenetics
- evolution
- evolutionary psychology
- fetal alcohol syndrome
- fitness
- focal hand dystonia
- genes
- hemorrhage
- heritability
- heterozygous
- homozygous
- ischemia
- kin selection
- Lamarckian evolutions
- migrate
- monozygous
- mutation
- myelination
- nerve growth factor (NGF)
- neurotrophin
- phantom limb
- phenylketonuria (PKU)
- proliferation
- recessive
- reciprocal altruism
- ribonucleic acid (RNA)
- sex-limited genes
- sex-linked genes
- stem cells
- stroke
- synaptogenesis
- tissue plasminogen activator (tPA)
Links
- ZeroToThree’s description of brain development (Links to an external site.)
- Neuroscience for Kids: Brain During Development (Links to an external site.)
Summary
The brain starts as a primitive streak. The steak flattens into a plate. The middle of the p late deepens into a grove. Cells from each side of the grove zip it up into a neural tube. The cells inside the tube become the cortex, the spinal cord and all the structures of the brainstem and limbic system.